Ask a bunch of dirt bike riders the question, “is 2-stroke or 4-stroke faster?” and you’ll get different opinions from them. In fact, this question has been up for debate longer than I’ve been into dirt bikes.
In determining whether a two-stroke or four-stroke engine is faster, you must consider three factors: your riding ability, your riding style, and your knowledge of how these engines work.
A two-stroke engine only takes two stages or strokes to complete an engine cycle, so they accelerate faster than four-stroke engines. A four-stroke takes four phases or strokes to build more power, consistency, and higher top speed during riding.
What’s the difference between a 2-stroke and a 4-stroke engine?
How a four-stroke engine works
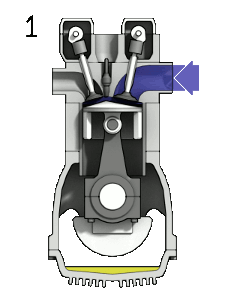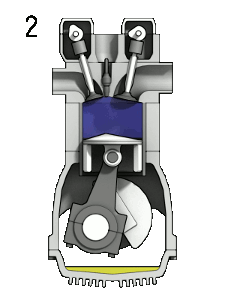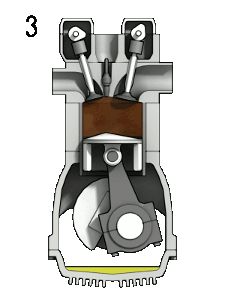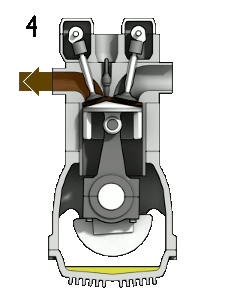
Image courtesy of Zephyris
In a four-stroke engine, the piston goes through four different stages or strokes before it completes a revolution:
Intake
- The air-fuel mixture enters the engine’s combustion chamber
- The piston moves from the cylinder’s Bottom Dead Center (BDC) to the Top Dead Center (TDC).
- The intake valve is opened, and the exhaust valve is closed
- The downward motion creates a low vacuum pressure inside the cylinder
- The air-fuel mixture moves toward the engine via the intake valve
Compression
- The piston continues moving from BDC to TDC. The intake and exhaust valves are closed at this point.
- The air-fuel mixture is trapped and further compressed in the cylinder by the upward motion of the piston
Combustion
- The spark plug, located between the intake and exhaust valves, ignites the air-fuel mixture
- A strong force pushes the piston to BDC and rotates the crankshaft, propelling your dirt bike to move forward
Exhaust
- The exhaust valve is now open
- The piston also resumes movement from BDC to TDC, which moves the spent air-fuel mixture from the combustion stroke out the exhaust valve
- The cycle repeats
The two-stroke engine only requires two strokes to power up a dirt bike. It has inlet and exhaust ports rather than an intake and exhaust valve found in four-stroke engines.
How a two-stroke engine works
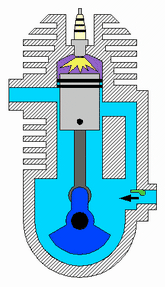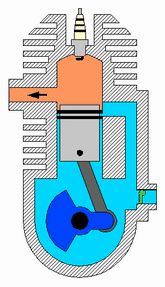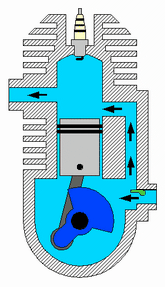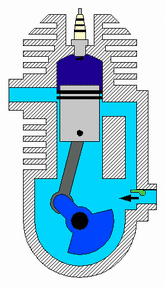
Image courtesy of A. Schierwagen
Here’s how a two-stroke engine works:
Compression
- The air-fuel mixture enters the chamber through the open inlet port.
- The piston moves upwards from BDC to TDC and compresses the air-fuel mixture.
- The spark plug ignites the fuel, powering up the engine.
Power
- The heated air-fuel mixture exerts high pressure on the piston, causing it to move downward.
- The movement exhausts the spent air-fuel mixture towards the exhaust port.
Two-stroke engine: Pros and Cons
Pros
Two-stroke dirt bikes are more popular for several reasons. For one, a two-stroke engine is smaller, so you won’t need to pull out everything to clean, repair, or maintain it.
Two-stroke engines are also easier to maintain. These engines have fewer wiring and moving parts, like camshafts, timing chains, and valves.
Since the engine has a less complicated design, it’s more lightweight than its counterpart.
A two-stroke engine can be as powerful as a four-stroke, especially its impressive power-to-weight ratio. The lighter your dirt bike is, the more power your engine can produce for you.
The fewer strokes required to power up a dirt bike’s engine allows it to provide quicker acceleration and power than its counterpart.
It has a five out of five mechanical efficiency rating because it creates little friction while running.
Lastly, dirt bikes with two-stroke engines are also cheaper, thanks to the lack of complicated mechanisms.
Cons
Two-stroke engines tend to have a shorter life span than four-stroke engines. The high, quick power produced by the engine tends to wear and tear the piston rings and the internal chamber.
The more you rev your engine, the faster it wears out. The higher-power-faster-acceleration feature seems like a Catch-22 on the technical side.
Most riders also complain about the loud noise and vibrations two-stroke engines make when riding. Some riders use dampeners and silencers to lessen the loud noise as a solution to this, though.
It’s also not as fuel efficient, despite having fewer strokes. Since both ports aren’t closed during the combustion stroke, some unburned charges leave the exhaust port, decreasing fuel efficiency.
The biggest downside to a two-stroke dirt bike is its high hydrocarbon emissions rate, due to the lack of inlet and exhaust valves. However, dirt bike manufacturers like Yamaha and KTM are introducing improved two-stroke bikes today with lower carbon emissions rates.
Four-stroke engine: Pros and Cons
Pros
One of the most unique features of four-stroke dirt bikes is their high torque at low RPM. The higher torque means your four-stroke dirt bike runs smoother and more stable at maximum speed.
Despite the more complicated mechanism of a four-stroke engine, it actually has a longer life than a two-stroke engine. The lubrication and cooling system of four-strokes prevent the cylinder and other parts from suffering wear and tear during the combustion process.
Four-stroke engines are also more fuel-efficient than their counterparts. The intake and exhaust valves keep the fuel losses in control and improve the fuel-to-power ratio of the dirt bike.
Lastly, four-stroke dirt bikes are your best bet if you want something more environment-friendly. It has a separate combustion chamber and lubrication system that ensures:
- Engine only burns fuel
- Oil is used separately
- Fewer dangerous carbon emissions emitted
Cons
Four-stroke engines require more complex parts for their four-process engine cycle, and designing the placement of these parts requires careful planning.
The complex design makes four-stroke dirt bikes more expensive than two-stroke motorcycles. Assembling the parts can be time-consuming and costly, not to mention the number of parts needed to keep your dirt bike running as advertised.
A four-stroke also requires more maintenance and servicing.
Is 2-stroke or 4-stroke faster?

Two-stroke dirt bikes accelerate faster on ignition because of their shorter strokes and lighter build. That also means two-stroke dirt bikes wear out quicker than their counterparts.
While four-stroke dirt bikes take longer to complete an engine cycle, one cannot deny the power they produce. In dirt bike racing, more power means sustained top speed and acceleration in the long run.
So technically, both can be fast – the two-stroke variety only happens to reach high speeds faster.
Should I go for a two-stroke or four-stroke dirt bike?
Choosing the best engine type depends entirely on your riding preference and riding skills.
A two-stroke dirt bike will offer you speed and thrills. They tend to “dance” around due to their lightweight build, but that’s something a few practices can fix.
For smooth and stable riding, a four-stroke dirt bike is a way to go. Its torque, power, and better stability make up for the lack of initial speed. Due to their heavier build, four-strokes don’t dance on the track like two-strokes.
Maintenance is a bit more expensive, but their life span is longer.
Wrapping up
| Two-stroke | Four-stroke | |
| Pros | Weighs less Easier to maintain Quicker acceleration Faster than four-stroke Mechanically efficient Cheaper | Higher torque More power = sustained speed and acceleration in the long run Longer lifespan Fuel-efficient More stable to ride Environment-friendly |
| Cons | Shorter life span Loud noise and vibration Not fuel-efficient High hydrocarbon emission rate (especially for older models) | Complex design and placement of parts Complicated to maintain More expensive Requires regular maintenance and servicing |
Although both can offer high speeds on the road, a two-stroke engine delivers speed faster than a four-stroke engine. This is because it only takes two processes or strokes for a two-stroke engine to complete a full crankshaft revolution.
Choosing the right engine type depends strongly on your riding skills and riding style. A four-stroke dirt bike might take longer to rev but builds more power, while a two-stroke engine can accelerate faster but is less stable for long rides.



